Nanobubbles penetrate and physically remove microbial
biofilm on surfaces while preventing re-formation

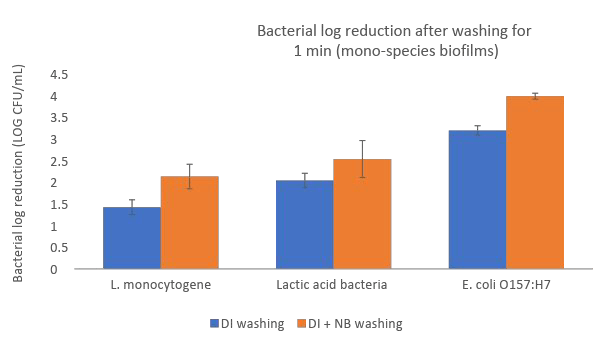
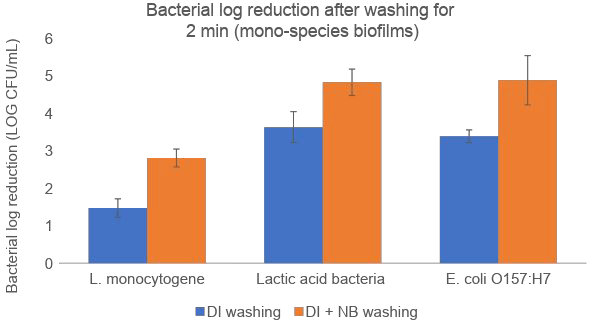
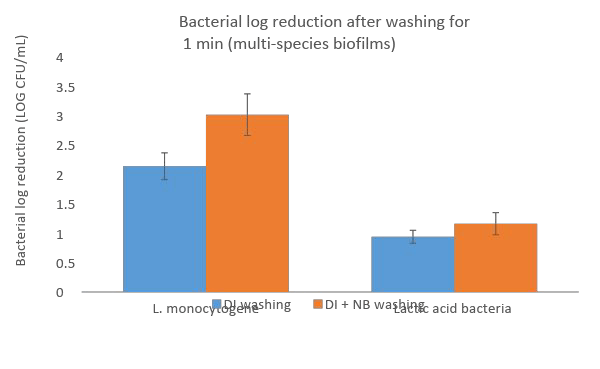
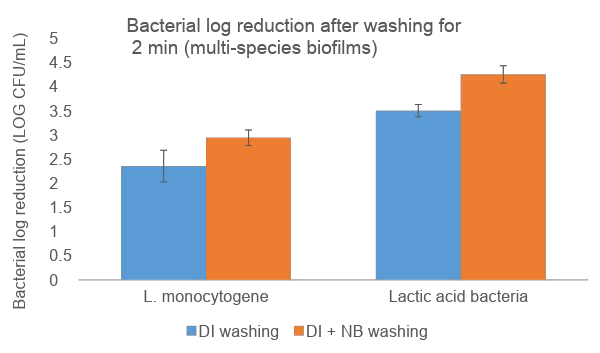
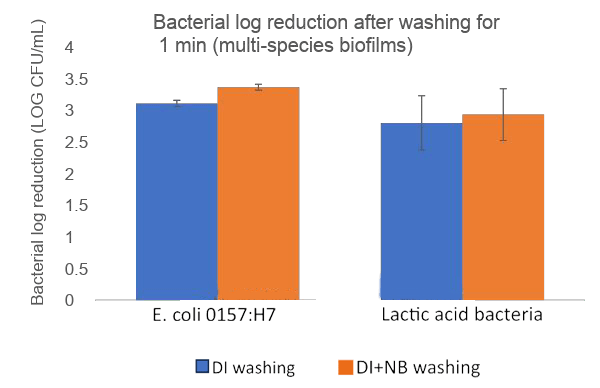
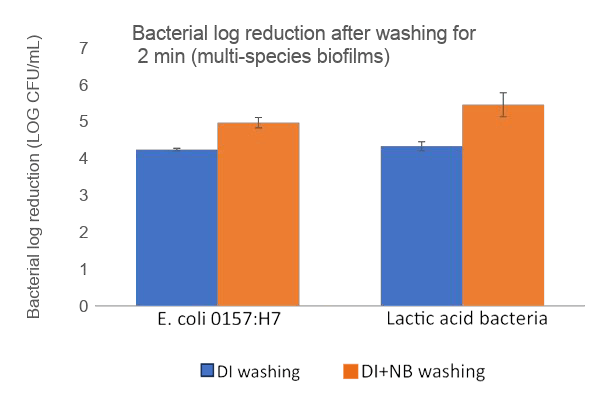
Nanobubbles penetrate into organic material to inactivate microbial biofilms and increase bacterial detachment.

Nanobubbles damage reciprocal interactions among microbial species, destabilize the biofilm network structure and inhibit formation.
Nanobubbles produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), consisting primarily of hydroxyl radicals to eliminate hard-to-kill pathogens and reduce the use of chemicals.
Nanobubbles control biofilm formation in pipes by directly acting on microbes and indirectly acting on water quality (TO, COD, BOD)..

Nanobubbles Increased zeta-potential attracts and collects opposite charged sludge particles and better penetrates boundary layers on opposite charged surfaces.
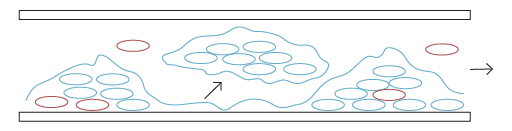
STEP 1: Clean pipe surfaces being conditioned.
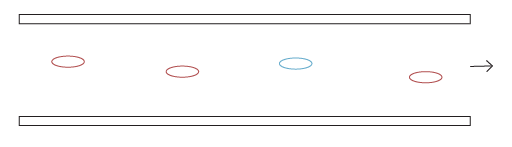
STEP 2: Microorganisms attach to surfaces and start to form a biofilm community of bacteria, fungi, yeasts and other microbial cells.
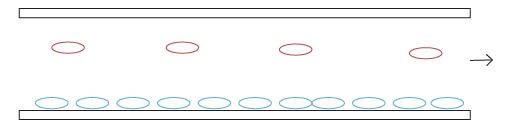
STEP 3: Cells are embedded in a self-produced matrix called extracellular polymer substances (EPS) and multiply.
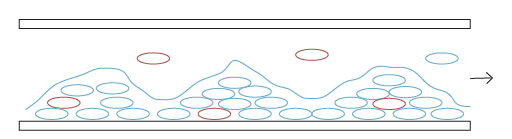
STEP 4: Microbial cells detach from biofilm as individual cells or as clumps and re-contaminate water.
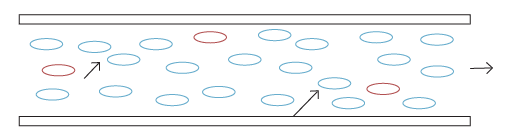
STEP 6: A clean system is achieved and maintained.